Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
荒木 康史; 家田 淳一
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(7), p.074705_1 - 074705_9, 2023/06
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)トポロジカル絶縁体は電子が波数空間でトポロジカル構造を持つことにより、様々な非自明な電磁応答現象を示す。一方で、現在用いられているインダクタ・キャパシタの動作原理は、マクスウェル方程式によって記述される古典電磁気学に基づいている。本研究では絶縁体中のトポロジカル電磁応答が、磁性体中の磁化ダイナミクスと組み合わさることにより、インダクタンス・キャパシタンスを生み出すことを示す。まず、トポロジカル場の理論に基づいて、複素インピーダンスを導出する理論的枠組みを提案する。次にその理論に基づき、接合系のセットアップでインダクタンス・キャパシタンスが発現することを示す。金属磁性体における創発インダクタンスに関する先行研究と比較すると、トポロジカル絶縁体はジュール熱を抑制できるため、素子内での電力損失を大幅に抑制することができる。これによって、トポロジカル電磁応答に起因したインダクタンスは弱電流・高周波数での動作を可能とし、更に電力効率の面でも高い品質係数(Q値)を実現できることを示す。
中山 勝政*; 鈴木 渓
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 430, p.379_1 - 379_9, 2023/04
本来のカシミール効果は連続時空上に存在する量子場から創発する物理現象であり、理論的にも信頼性の高い定式化が達成されているが、「格子」上に定義された空間(例えば、固体の結晶構造など)において、カシミール効果に相当する物理現象を定式化し、その性質を明らかにすることは重要なテーマである。本会議録では、格子上の様々な量子場に起因するカシミール効果の性質に関する近年の研究成果について報告する。まず、格子空間上のカシミールエネルギーを定義し、格子上のフェルミ粒子の一種であるウィルソン・フェルミオンによるカシミール効果が連続時空上のディラック粒子によるものと極めて似た性質となることを示す。さらに、Cd As
As やNa
やNa Biなどのディラック半金属を記述する有効ハミルトニアンを用いた解析により、この系のカシミールエネルギーが半金属薄膜の厚さの関数として振動することを示す。また、電子系に磁場をかけることで生じるランダウ量子化による影響や格子上の非相対論的量子場によるカシミール効果の性質についても報告する。
Biなどのディラック半金属を記述する有効ハミルトニアンを用いた解析により、この系のカシミールエネルギーが半金属薄膜の厚さの関数として振動することを示す。また、電子系に磁場をかけることで生じるランダウ量子化による影響や格子上の非相対論的量子場によるカシミール効果の性質についても報告する。
石川 力*; 中山 勝政*; 鈴木 渓
Physical Review D, 104(9), p.094515_1 - 094515_11, 2021/11
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:37.94(Astronomy & Astrophysics)「ウィルソン・フェルミオン」と呼ばれる格子上のフェルミ粒子に対する近藤効果を記述する模型を構築し、様々な物理現象の予言・解明を行った。模型として、軽いウィルソン・フェルミオンと重いフェルミオンとの4点相互作用を含むカイラルGross-Neveu模型に対する平均場アプローチを用いた。結果として、ゼロ質量のウィルソン・フェルミオンからなる有限密度媒質において近藤効果が実現可能であることを示し、それに伴う近藤凝縮と軽いフェルミオン対の凝縮(スカラー凝縮)との共存相が存在可能であることを示した。このとき、スカラー凝縮が消える臨界的な化学ポテンシャルの値は近藤効果によってシフトする。さらに、負質量を持つウィルソン・フェルミオンにおいては、パリティ対称性が自発的に破れた相(Aoki phase)が生じることが知られているが、Aoki phaseが生じるパラメータ領域近傍で近藤効果も増幅されることを示した。本研究の発見は、ディラック半金属,トポロジカル絶縁体などの物質や、将来的な格子シミュレーションにおける不純物の役割を明らかにするために役立つことが期待される。
石川 力*; 中山 勝政*; 鈴木 渓
Physical Review Research (Internet), 3(2), p.023201_1 - 023201_23, 2021/06
カシミール効果は、何らかの粒子のゼロ点エネルギーが2枚の平行平板の存在によって歪められることによって生じる物理現象である。格子上の自由度においては、エネルギーと運動量の分散関係はブリルアンゾーンの範囲で周期性を持つため、それに対応してカシミール効果も変化するはずである。本研究では、ナイーブ・フェルミオン,ウィルソン・フェルミオン,(メビウス・ドメインウォール・フェルミオン定式化に基づく)オーバーラップ・フェルミオンなどの格子フェルミオン系におけるカシミール効果の性質を理論的に調べた。特に、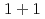 ,
, 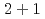 ,
, 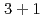 次元において周期境界条件または反周期境界条件を持つ系について系統的な解析を行った。中でも、ナイーブ・フェルミオン,負質量を持つウィルソン・フェルミオン,domain-wall heightが大きい場合のオーバーラップ・フェルミオンなどの系において、奇数格子と偶数格子の間でカシミールエネルギーの大きさが振動する現象が見られた。この振動現象は、高運動量を持つ自由度(ダブラー)の存在に起因している。このような新奇なカシミール効果は、トポロジカル絶縁体のような物性系の実験や格子シミュレーションによって将来的に検証されることが期待される。
次元において周期境界条件または反周期境界条件を持つ系について系統的な解析を行った。中でも、ナイーブ・フェルミオン,負質量を持つウィルソン・フェルミオン,domain-wall heightが大きい場合のオーバーラップ・フェルミオンなどの系において、奇数格子と偶数格子の間でカシミールエネルギーの大きさが振動する現象が見られた。この振動現象は、高運動量を持つ自由度(ダブラー)の存在に起因している。このような新奇なカシミール効果は、トポロジカル絶縁体のような物性系の実験や格子シミュレーションによって将来的に検証されることが期待される。
石川 力*; 中山 勝政*; 鈴木 渓
Physics Letters B, 809, p.135713_1 - 135713_7, 2020/10
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:76.76(Astronomy & Astrophysics)本論文では、相互作用のない格子フェルミオンにおけるカシミールエネルギーの定義を世界で初めて提案する。我々はこの定義を用いることで、空間方向に周期境界条件や半周期境界条件が課された1+1次元時空におけるナイーブ・フェルミオン,ウィルソン・フェルミオン,(メビウス・ドメインウォール・フェルミオン定式化に基づく)オーバーラップ・フェルミオンに対するカシミール効果の性質を調べた。ナイーブ・フェルミオンにおいては、奇数個・偶数個の格子に対してカシミールエネルギーが交互に振動するという結果が得られた。ウィルソン・フェルミオンにおいては、格子サイズが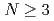 の領域で、連続理論のディラック粒子におけるカシミールエネルギーとよく一致する結果が得られた。この結果は、格子シミュレーションによってカシミール効果を測定する際に、ウィルソン・フェルミオンによる格子正則化を用いることで離散化誤差をよく制御できることを意味している。さらに、(メビウス・ドメインウォール・フェルミオン定式化に基づく)オーバーラップ・フェルミオンはトポロジカル絶縁体の表面モードに対応しており、様々なモデルパラメータ依存性も調べた。これらの発見は、対応する格子構造を持つ物性系や、格子上の数値シミュレーションによっても検証されることが期待される。
の領域で、連続理論のディラック粒子におけるカシミールエネルギーとよく一致する結果が得られた。この結果は、格子シミュレーションによってカシミール効果を測定する際に、ウィルソン・フェルミオンによる格子正則化を用いることで離散化誤差をよく制御できることを意味している。さらに、(メビウス・ドメインウォール・フェルミオン定式化に基づく)オーバーラップ・フェルミオンはトポロジカル絶縁体の表面モードに対応しており、様々なモデルパラメータ依存性も調べた。これらの発見は、対応する格子構造を持つ物性系や、格子上の数値シミュレーションによっても検証されることが期待される。
 Te
Te
Shikin, A. M.*; Estyunin, D. A.*; Klimovskikh, I. I.*; Filnov, S. O.*; Kumar, S.*; Schwier, E. F.*; 宮本 幸治*; 奥田 太一*; 木村 昭夫*; 黒田 健太*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 10, p.13226_1 - 13226_13, 2020/08
被引用回数:59 パーセンタイル:96.43(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Modification of the gap at the Dirac point (DP) in axion antiferromagnetic topological insulator MnBi Te
Te and its electronic and spin structure have been studied by angle- and spin-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) under laser excitation at various temperatures, light polarizations and photon energies. We have distinguished both large and reduced gaps at the DP in the ARPES dispersions, which remain open above the N
and its electronic and spin structure have been studied by angle- and spin-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) under laser excitation at various temperatures, light polarizations and photon energies. We have distinguished both large and reduced gaps at the DP in the ARPES dispersions, which remain open above the N el temperature of
el temperature of 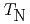 = 24.5 K. We propose that the gap above
= 24.5 K. We propose that the gap above 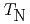 remains open due to a short-range magnetic field generated by chiral spin fluctuations. Spin-resolved ARPES, XMCD and circular dichroism ARPES measurements show a surface ferromagnetic ordering for the large gap sample and apparently significantly reduced effective magnetic moment for the reduced gap sample.
remains open due to a short-range magnetic field generated by chiral spin fluctuations. Spin-resolved ARPES, XMCD and circular dichroism ARPES measurements show a surface ferromagnetic ordering for the large gap sample and apparently significantly reduced effective magnetic moment for the reduced gap sample.
荒木 康史; 三澤 貴宏*; 野村 健太郎*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 2(2), p.023195_1 - 023195_11, 2020/05
We theoretically manifest that the edge of a quantum spin Hall insulator (QSHI), attached to an insulating ferromagnet (FM), can realize a highly efficient spin-to-charge conversion. Based on a one-dimensional QSHI-FM junction, the electron dynamics on the QSHI edge is analyzed, driven by a magnetization dynamics in the FM. Under a large gap opening on the edge from the magnetic exchange coupling, we find that the spin injection into the QSHI edge gets suppressed while the charge current driven on the edge gets maximized, demanded by the band topology of the one-dimensional helical edge states.
 V
V Te
Te
角田 一樹*; 鹿子木 将明*; Reimann, J.*; Nurmamat, M.*; 後藤 伸一*; 竹田 幸治; 斎藤 祐児; Kokh, K. A.*; Tereshchenko, O. E.*; G dde, J.*; et al.
dde, J.*; et al.
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 21(9), p.093006_1 - 093006_8, 2019/09
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:65.02(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We systematically investigate the magnetic, structural and electronic properties and the ultrafast carrier dynamics in a series of V-doped Sb Te
Te samples of composition Sb
samples of composition Sb V
V Te
Te with x = 0, 0.015 and 0.03. Element specific X-ray magnetic circular dichroism signifies that the ferromagnetism of V-doped Sb
with x = 0, 0.015 and 0.03. Element specific X-ray magnetic circular dichroism signifies that the ferromagnetism of V-doped Sb Te
Te is governed by the p-d hybridization between the host carrier and the magnetic dopant. Time- and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy has revealed that the V impurity induced states underlying the topological surface state (TSS) add scattering channels that significantly shorten the duration of transient surface electrons down to 100 fs scale. This is in a sharp contrast to the prolonged duration reported for pristine samples though the TSS is located inside the bulk energy gap of the host in either magnetic or non-magnetic cases. It implies the presence of a mobility gap in the bulk energy gap region of the host material.
is governed by the p-d hybridization between the host carrier and the magnetic dopant. Time- and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy has revealed that the V impurity induced states underlying the topological surface state (TSS) add scattering channels that significantly shorten the duration of transient surface electrons down to 100 fs scale. This is in a sharp contrast to the prolonged duration reported for pristine samples though the TSS is located inside the bulk energy gap of the host in either magnetic or non-magnetic cases. It implies the presence of a mobility gap in the bulk energy gap region of the host material.
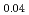 (Sb
(Sb Bi
Bi )
)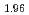 Te
Te
Ye, M.*; Xu, T.*; Li, G.*; Qiao, S.*; 竹田 幸治; 斎藤 祐児; Zhu, S.-Y.*; Nurmamat, M.*; 角田 一樹*; 石田 行章*; et al.
Physical Review B, 99(14), p.144413_1 - 144413_7, 2019/04
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:56.27(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigate the microscopic origin of ferromagnetism coupled with topological insulators in V-doped (Sb,Bi) Te
Te employing X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and angle-resolved two-photon photoemission spectroscopies, combined with first-principles calculations. We found an magnetic moment at the Te site anti-parallel to that of the V and Sb sites, which plays a key role in the ferromagnetic order. We ascribe it to the hybridization between Te 5
employing X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and angle-resolved two-photon photoemission spectroscopies, combined with first-principles calculations. We found an magnetic moment at the Te site anti-parallel to that of the V and Sb sites, which plays a key role in the ferromagnetic order. We ascribe it to the hybridization between Te 5 and V 3
and V 3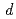 majority spin states at the Fermi energy, consistent with the Zener-type
majority spin states at the Fermi energy, consistent with the Zener-type  -
-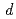 exchange interaction scenario. The substitution of Bi for Sb suppresses the bulk ferromagnetism by introducing extra electron carriers in the majority spin channel of the Te
exchange interaction scenario. The substitution of Bi for Sb suppresses the bulk ferromagnetism by introducing extra electron carriers in the majority spin channel of the Te  states that compensates the antiparallel magnetic moment on the Te site. Our findings reveal important clues to designing magnetic topological insulators with higher Curie temperature that work under ambient conditions.
states that compensates the antiparallel magnetic moment on the Te site. Our findings reveal important clues to designing magnetic topological insulators with higher Curie temperature that work under ambient conditions.
Shikin, A. M.*; Estyunin, D. A.*; Surnin, Yu. I.*; Koroleva, A. V.*; Shevchenko, E. V.*; Kokh, K. A.*; Tereshchenko, O. E.*; Kumar, S.*; Schwier, E. F.*; 島田 賢也*; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 9(1), p.4813_1 - 4813_17, 2019/03
被引用回数:19 パーセンタイル:71.48(Multidisciplinary Sciences)A new kind of magnetically-doped antiferromagnetic (AFM) topological insulators (TIs), Bi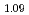 Gd
Gd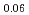 Sb
Sb Te
Te , has been studied by angle-resolved photoemission, superconducting magnetometry (SQUID) and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD). It has been shown that this TI is characterized by the Dirac gap at the Fermi level. In the paramagnetic phase, a surface magnetic layer is supposed to develop, where the coupling between the Gd magnetic moments is mediated by the topological surface states (TSSs). This assumption can be confirmed by opening a gap at the Dirac point indicated by the surface-sensitive ARPES, a weak hysteresis loop measured by SQUID, the XMCD showing a surface magnetic moment and the temperature dependence of electrical resistance demonstrating a mid-gap semiconducting behavior, which correlates with the temperature dependence of the surface magnetization and confirms the conclusion that only TSSs are located at the Fermi level.
, has been studied by angle-resolved photoemission, superconducting magnetometry (SQUID) and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD). It has been shown that this TI is characterized by the Dirac gap at the Fermi level. In the paramagnetic phase, a surface magnetic layer is supposed to develop, where the coupling between the Gd magnetic moments is mediated by the topological surface states (TSSs). This assumption can be confirmed by opening a gap at the Dirac point indicated by the surface-sensitive ARPES, a weak hysteresis loop measured by SQUID, the XMCD showing a surface magnetic moment and the temperature dependence of electrical resistance demonstrating a mid-gap semiconducting behavior, which correlates with the temperature dependence of the surface magnetization and confirms the conclusion that only TSSs are located at the Fermi level.
 Te
Te
Ye, M.*; Li, W.*; Zhu, S.-Y.*; 竹田 幸治; 斎藤 祐児; Wang, J.*; Pan, H.*; Nurmamat, M.*; 角田 一樹*; Ji, F.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 6, p.8913_1 - 8913_7, 2015/11
被引用回数:52 パーセンタイル:89.95(Multidisciplinary Sciences)磁性元素を添加したトポロジカル絶縁体は、量子異常ホール効果や無散逸伝導などの魅力的な現象の発現が予言され、低消費電力スピンデバイスの開発につながっていくものと期待されている。既に、いくつかの磁性添加トポロジカル絶縁体で長距離磁気秩序が確認されている。しかし、量子異常ホール効果の発現は、極低温におけるCrを添加した(Sb,Bi) Te
Te 系に限られており、強磁性の微視的な起源はほとんど分かっていない。そこで、今回、X線磁気円二色性実験による元素選択的研究を行うことにより、本物質系の強磁性は、母体の正孔キャリアーを媒介としたものであり、Crの3d電子とSbやTeのp電子の相互作用が極めて重要であることを明らかにした。この結果は、異常量子ホール素子の実現に向けても重要である。
系に限られており、強磁性の微視的な起源はほとんど分かっていない。そこで、今回、X線磁気円二色性実験による元素選択的研究を行うことにより、本物質系の強磁性は、母体の正孔キャリアーを媒介としたものであり、Crの3d電子とSbやTeのp電子の相互作用が極めて重要であることを明らかにした。この結果は、異常量子ホール素子の実現に向けても重要である。
河裾 厚男; Li, H.; 前川 雅樹; 阿部 浩之; 宮下 敦巳
no journal, ,
トポロジカル絶縁体の表面では、カイラルスピン構造が形成されており、運動量とスピンの方向が常に垂直に保たれている。そこで、表面平行方向に電流を印加することで、表面電子がスピン偏極することが考えられる。しかし、バンドギャップが非常に狭いことや、電気的に活性な固有欠陥の生成などにより、バルクの絶縁状態が保持されているとは限らず、表面電気伝導をバルクから分離して観測することは容易ではない。本研究では、表面電子スピンを高感度に捉えることができるスピン偏極陽電子ビームを用いて、トポロジカル絶縁体の一つとされているBi Sb
Sb 表面の電流誘起スピン偏極を観測した。その結果、Sb組成比がトポロジカル絶縁相のx=0.06-0.2になるとスピン偏極率は4-5%となり、さらにSb組成比x
表面の電流誘起スピン偏極を観測した。その結果、Sb組成比がトポロジカル絶縁相のx=0.06-0.2になるとスピン偏極率は4-5%となり、さらにSb組成比x 0.22では、表面電子のスピン偏極率は検出限界以下であった。これらはトポロジカル絶縁相の発現と消失に対応している可能性がある。
0.22では、表面電子のスピン偏極率は検出限界以下であった。これらはトポロジカル絶縁相の発現と消失に対応している可能性がある。
荒木 康史; 三澤 貴宏*; 野村 健太郎*
no journal, ,
We present our theoretical work on spin pumping into a two-dimensional (2D) quantum spin Hall inslator (QSHI). Recent theories and experiments have demonstrated the QSHI phase in a monolayer of transition metal dichalcogenide 1T'-WTe2, which can be easily engineered in contrast to traditionally-known HgTe/CdTe and InAs/GaSb quantum wells. While the theory of spin pumping is well established in normal metals by focusing on the spin-dependent electron scattering at the interface, it is unreliable for topologically nontrivial interfaces in such systems. In the present work, we consider a junction of a ferromagnet and a 2D QSHI at its 1D edge, and demonstrate the pumping of angular momentum from the spin-precessing ferromagnet into the QSHI. Using the Floquet theory for the electrons on the helical edge states, we analytically show that the time-periodic precession of the magnetization drives a charge current on the edge, for the whole range of precession frequency. This edge current can be regarded as a consequence of the inverse spin Hall effect intrinsic to the QSHI, which converts the injected spin current into a transverse charge current. By varying the precession frequency of the magnetization and the coupling strength at the junction, we find a clear crossover between two regimes: the adiabatic regime, where the slow magnetization precession drives a quantized pumping, and the resonant regime, where the fast precession leads to a suppressed pumping. We also incorporate the effect of orbital dependence in the exchange coupling at the edge, and show numerically that it shifts the crossover point between the adiabatic and resonant regimes.
荒木 康史; 三澤 貴宏*; 野村 健太郎*
no journal, ,
The two-dimensional quantum spin Hall insulator (2D QSHI) is the most primitive but quite important realization of topological insulator. It shows the helical edge states protected by time-reversal symmetry, whereas the quantized spin Hall conductivity in the bulk. In the present work, we theoretically investigate the spin pumping from a precessing ferromagnet into a 2D QSHI thoroughly from the adiabatic to nonadiabatic regimes, both analytically and numerically. We analytically treat the dynamics of the edge-state electrons coupled to the precessing ferromagnet by the Floquet theory, and derive the pumped current as a function of the exchange energy and the precession frequency. We find that a heat bath for the edge electrons governs the transition between the adiabatic and nonadiabatic regime: when the edge electrons are coupled with a heat bath, their spin and energy can dissipate into the bath by a certain rate, eventually reaching a periodic steady state. The pumped current on the becomes quantized when the exchange energy exceeds the dissipation rate. We also calculate the edge current numerically on the 2D lattice model, and find that the bulk states in the QSHI effectively serves as the heat bath for the edge electrons.
荒木 康史; 三澤 貴宏*; 野村 健太郎*
no journal, ,
We present our theoretical work on spin pumping into a two-dimensional (2D) quantum spin Hall inslator (QSHI). QSHI is a topological insulator in 2D exhibiting gapless helical edge stats, which are responsible for the quantized spin Hall conductivity. Recent theories and experiments have demonstrated the QSHI phase in a monolayer of transition metal dichalcogenide 1T'-WTe2, which can be easily engineered in contrast to traditionally-known HgTe/CdTe and InAs/GaSb quantum wells. While the theory of spin pumping is well established in normal metals by focusing on the spin-dependent electron scattering at the interface, it is unreliable for topologically nontrivial interfaces in such systems. In the present work, we consider a junction of a ferromagnet and a 2D QSHI at its 1D edge, and demonstrate the pumping of angular momentum from the spin-precessing ferromagnet into the QSHI. Using the Floquet theory for the electrons on the helical edge states, we analytically show that the time-periodic precession of the magnetization drives a charge current on the edge, for the whole range of precession frequency. This edge current can be regarded as a consequence of the inverse spin Hall effect intrinsic to the QSHI, which converts the injected spin current into a transverse charge current. By varying the precession frequency of the magnetization and the coupling strength at the junction, we find a clear crossover between two regimes: the adiabatic regime, where the slow magnetization precession drives a quantized pumping, and the resonant regime, where the fast precession leads to a suppressed pumping. We also incorporate the effect of orbital dependence in the exchange coupling at the edge, and show numerically that it shifts the crossover point between the adiabatic and resonant regimes.
荒木 康史; 三澤 貴宏*; 野村 健太郎*
no journal, ,
We present our theoretical work on dynamical spin-to-charge conversion at the edge of a quantum spin Hall insulator (QSHI), namely a two-dimensional topological insulator with helical edge states. Interconversion between spin- and charge-related quantities has been a key idea in making use of magnetic materials, especially in the context of spintronics. QSHI is a typical system showing a universal charge-to-spin conversion behavior, namely the quantum spin Hall effect, whereas the spin-to-charge conversion therein is still not clearly understood. At a lateral heterojunction of a ferromagnet (FM) and a QSHI, it has been theoretically demonstrated that magnetization dynamics induces a charge current along the edge of QSHI; however, its mechanism from the viewpoint of spin-to-charge conversion still remains to be clarified. In order to understand the spin transfer and the spin-to-charge conversion mechanism in QSHI, we investigate the many-body dynamics of the electrons under the magnetization dynamics at the QSHI-FM junction. We analytically treat the electron dynamics in terms of the Floquet-Keldysh formalism, and compare two physical quantities present on the edge: the spin injection rate from the FM into the QSHI, and the charge current induced along the edge. Whereas the edge current seen in the previous works is reproduced, we find that it is not proportional to the spin injection rate, especially when the exchange interaction at the junction is strong enough. This relation implies that the spin-to-charge conversion in this system cannot be considered as the inverse spin Hall effect, while it can be rather seen as the inverse Edelstein effect, in which an electron spin accumulation at the junction is converted to a charge current. We also focus on the energy transfer at the junction, and interpret this phenomenon in terms of magnon exchange.
石川 力*; 中山 勝政*; 鈴木 渓
no journal, ,
本講演では、相互作用のない格子フェルミオンにおけるカシミールエネルギーの定義を提案する。我々はこの定義を用いることで、空間方向に周期境界条件や半周期境界条件が課された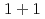 次元時空におけるナイーブ・フェルミオン,ウィルソン・フェルミオン,(メビウス・ドメインウォール・フェルミオン定式化に基づく)オーバーラップ・フェルミオンに対するカシミール効果の性質を調べた。ナイーブ・フェルミオンにおいては、奇数個・偶数個の格子に対してカシミールエネルギーが交互に振動するという結果が得られた。ウィルソン・フェルミオンにおいては、格子サイズが
次元時空におけるナイーブ・フェルミオン,ウィルソン・フェルミオン,(メビウス・ドメインウォール・フェルミオン定式化に基づく)オーバーラップ・フェルミオンに対するカシミール効果の性質を調べた。ナイーブ・フェルミオンにおいては、奇数個・偶数個の格子に対してカシミールエネルギーが交互に振動するという結果が得られた。ウィルソン・フェルミオンにおいては、格子サイズが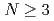 の領域で、連続理論のディラック粒子におけるカシミールエネルギーとよく一致する結果が得られた。この結果は、格子シミュレーションによってカシミール効果を測定する際に、ウィルソン・フェルミオンによる格子正則化を用いることで離散化誤差をよく制御できることを意味している。さらに、(メビウス・ドメインウォール・フェルミオン定式化に基づく)オーバーラップ・フェルミオンはトポロジカル絶縁体の表面モードに対応しており、様々なモデルパラメータ依存性も調べた。これらの発見は、対応する格子構造を持つ物性系や、格子上の数値シミュレーションによっても検証されることが期待される。
の領域で、連続理論のディラック粒子におけるカシミールエネルギーとよく一致する結果が得られた。この結果は、格子シミュレーションによってカシミール効果を測定する際に、ウィルソン・フェルミオンによる格子正則化を用いることで離散化誤差をよく制御できることを意味している。さらに、(メビウス・ドメインウォール・フェルミオン定式化に基づく)オーバーラップ・フェルミオンはトポロジカル絶縁体の表面モードに対応しており、様々なモデルパラメータ依存性も調べた。これらの発見は、対応する格子構造を持つ物性系や、格子上の数値シミュレーションによっても検証されることが期待される。
石川 力*; 中山 勝政*; 鈴木 渓
no journal, ,
従来から知られている近藤効果は、金属中の伝導電子と局在不純物間の相互作用によって生じる量子現象である。近年では、ディラック半金属やトポロジカル絶縁体,高密度クォーク物質のような「相対論的」フェルミオンを含む系における近藤効果も注目されている。特に、2013年に初めて予言されたQCD近藤効果は、有限密度クォーク物質中の不純物(ヘビー)クォークによって誘起されることが期待される現象である。しかし、QCD近藤効果が量子色力学(QCD)のどのパラメータ領域で実現するのか、さらに格子QCDシミュレーションによってどのように検証され得るかはまだ明らかでなく、将来的な課題となっている。本講演では、赤外領域でディラック粒子として振る舞う格子フェルミオンの一例としてウィルソン・フェルミオンに注目し、有効模型を用いて近藤効果が生じることを示す。さらに、格子系に特有の性質、他の非摂動効果との競合現象、格子シミュレーションへの実装における問題点などを議論する。
荒木 康史; 家田 淳一
no journal, ,
We theoretically propose novel functionalities of inductance and capacitance in heterostructures of topological insulators and magnets. Topological insulators show anomalous responses between electricity and magnetism, which are described not by the conventional Maxwell's equations, but by topological quantum field theory. Based on topological quantum field theory, we establish a unified theoretical framework applicable in arbitrary dimensions, to extract inductance and capacitance in topological insulators. We demonstrate the emergence of inductance and capacitance in several magnetic heterostructure setups, and show their advantages in achieving high operation frequency and high power efficiency.
荒木 康史; 家田 淳一
no journal, ,
We theoretically propose novel functionalities of inductance and capacitance in heterostructures of topological insulators and magnets. Topological insulators show anomalous responses between electricity and magnetism, which are described not by the conventional Maxwell's equations, but by topological quantum field theory. Based on topological quantum field theory, we establish a unified theoretical framework applicable in arbitrary dimensions, to extract inductance and capacitance in topological insulators. We demonstrate the emergence of inductance and capacitance in several magnetic heterostructure setups, and show their advantages in achieving high operation frequency and high power efficiency.
杉本 聡志*; 荒木 康史; 高橋 有紀子*; 家田 淳一; 葛西 伸哉*
no journal, ,
重金属・強磁性体ヘテロ構造に生じるスピン軌道トルク(SOT)は、磁化の電流操作手法における基幹技術のひとつである。一方で、従来型SOTには面直方向の対称性の破れに起因する不動点(invariant point)が存在し、垂直磁化膜の磁化反転プロセスにおいて終状態を制御できない問題(nondeterministic switching)が指摘されてきた。このような幾何学的制約に対し、近年、WTe や
や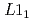 -CuPt/CoPtといった低対称性界面を使用した、新規SOT制御手法が注目されている。本研究では、C3v点群対称性を示すトポロジカル絶縁体Bi
-CuPt/CoPtといった低対称性界面を使用した、新規SOT制御手法が注目されている。本研究では、C3v点群対称性を示すトポロジカル絶縁体Bi Te
Te 薄膜界面に対し、楔形構造化等に起因するC1点群への対称性低下(symmetry reduction)を実現することで、強い異方性を示すSOTの生成に成功した。このような対称性を低下させる摂動下では、従来の直交方向への偏極成分(y-DL)に加え、面直成分(z-DL, z-FL)と平行成分(x-DL)へのSOT生成が新たに導出された。この異方的SOTを採用し、磁気共鳴状態における特異な非相反性と、電流誘起磁化反転における極性依存性が実験的にも観測された。
薄膜界面に対し、楔形構造化等に起因するC1点群への対称性低下(symmetry reduction)を実現することで、強い異方性を示すSOTの生成に成功した。このような対称性を低下させる摂動下では、従来の直交方向への偏極成分(y-DL)に加え、面直成分(z-DL, z-FL)と平行成分(x-DL)へのSOT生成が新たに導出された。この異方的SOTを採用し、磁気共鳴状態における特異な非相反性と、電流誘起磁化反転における極性依存性が実験的にも観測された。